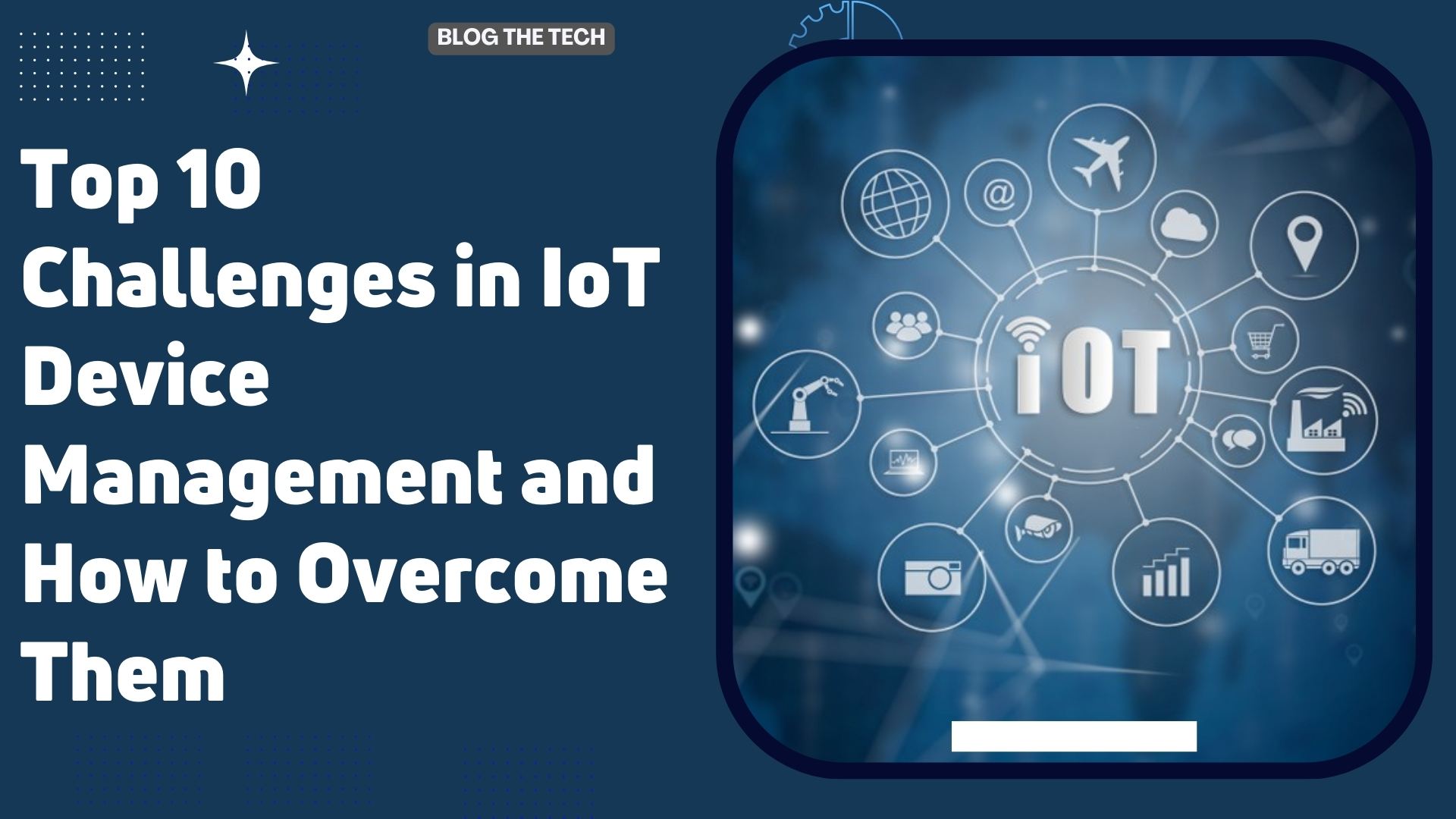
As the number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices continues to grow, managing them becomes increasingly complex. IoT devices are often connected to the internet, making them vulnerable to cyber-attacks, and they are manufactured by different companies, using different communication protocols.
The sheer volume of data generated by IoT devices can be overwhelming, and their limited lifespan requires careful planning for replacement or upgrades. Managing these devices effectively requires careful consideration of the top challenges in IoT device management.
In this article, we will explore the key challenges and strategies to overcome them.
1. Data management:
IoT devices generate a vast amount of data, which can be challenging to manage effectively. Managing IoT device data involves collecting, storing, analyzing and visualizing data. Data management is crucial to enable effective decision-making and to ensure that data is secure.
To manage IoT data, organizations should implement a robust data management strategy. This includes implementing data governance policies, ensuring data quality, and providing secure data storage. Additionally, IoT device management platforms should provide real-time data visualization and analytics capabilities, enabling users to make data-driven decisions.
2. Security challenges:
With the increase in the number of connected devices, security is a primary concern in IoT device management. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in the device’s software to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, causing severe damage to individuals and organizations.
To mitigate these risks, IoT devices must be secured using robust security protocols. This includes implementing strong encryption, secure booting, and secure communication protocols. Built-in security features such as firmware updates and secure boot mechanisms should also be provided. Additionally, regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing should be conducted to identify and remediate security gaps.
3. Device interoperability:
IoT devices are manufactured by different companies and use different communication protocols, making it challenging to ensure that devices work together seamlessly. Interoperability issues can lead to device failure, security vulnerabilities, and reduced productivity.
To overcome interoperability challenges, IoT device management systems should use open standards and protocols such as MQTT, CoAP, and RESTful APIs. These protocols ensure that devices can communicate with each other and with cloud-based systems, regardless of the manufacturer.
Additionally, easy integration with other systems such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM) systems should be provided.
4. Scalability:
As the number of IoT devices increases, managing them becomes increasingly difficult. Scalability is crucial to ensure that systems can handle large volumes of data, devices, and users.
To achieve scalability, IoT device management systems should leverage cloud computing and edge computing technologies. These technologies enable the processing and storage of large amounts of data and allow for distributed computing across multiple devices.
Additionally, containerization and microservices architectures enable IoT device management systems to be easily scaled up or down depending on the demand.
5. Device configuration:
Configuring IoT devices can be a complex and time-consuming process. Ensuring that each device is correctly configured is essential for managing devices effectively.
To simplify device configuration, IoT device management systems should use over-the-air (OTA) device management. OTA enables remote device management, configuration, and firmware updates. Additionally, automated configuration and provisioning tools should be provided, reducing the manual configuration process.
6. Device monitoring:
Monitoring IoT devices is critical to identify issues, ensure uptime, and optimize performance. However, monitoring thousands of devices can be overwhelming, and traditional monitoring tools may not be suitable for IoT device management.
To overcome this challenge, IoT device management platforms should provide real-time device monitoring and alerts. This includes the ability to monitor device health, network connectivity, and data transmission. Additionally, AI and machine learning-based analytics can identify patterns and anomalies, enabling proactive issue resolution.
7. Device maintenance:
IoT devices require regular maintenance to ensure that they continue to function correctly. This includes firmware updates, battery replacements, and other maintenance tasks. Ensuring that maintenance is performed regularly is essential for maintaining device reliability and preventing downtime.
To simplify device maintenance, IoT device management platforms should provide automated maintenance and update capabilities. These features enable devices to be remotely updated, reducing the need for manual updates.
8. Power management:
IoT devices are often powered by batteries or other portable power sources. Managing power consumption is critical to ensure that devices continue to function correctly and minimize the need for manual intervention.
To manage power consumption, IoT device management systems should provide power optimization features such as sleep modes and dynamic power management..
9. Device lifecycle management:
IoT devices have a limited lifespan, and it is essential to ensure that they are replaced or upgraded at the appropriate time. Device lifecycle management involves identifying when devices should be replaced or upgraded and planning for their retirement.
To manage device lifecycle, IoT device management platforms should provide asset management capabilities. This includes tracking device usage, identifying end-of-life devices, and planning for device replacement or upgrades.
Additionally, IoT device management platforms should provide remote device retirement and decommissioning capabilities, reducing manual intervention.
10. User experience:
Ensuring that users have a good experience with IoT devices is critical to their successful management. User experience includes ease of use, clear instructions, and providing support when needed.
To ensure a good user experience, IoT device management platforms should provide easy-to-use interfaces and clear instructions for device setup and management. Additionally, support channels such as chatbots or support portals should be provided to enable users to get assistance when needed.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, managing IoT devices is a complex task that requires careful planning and execution. Addressing the top challenges in IoT device management, including security, interoperability, scalability, device configuration, monitoring, maintenance, data management, power management, device lifecycle, and user experience, is essential for successful IoT device management.
By implementing strategies to overcome these challenges, organizations can ensure that their IoT devices are secure, reliable, and easy to manage, enabling them to harness the full potential of IoT technology.